Aug 11, 2025
Version 1
scDNA-scRNA-seq (SDR-seq) V.1
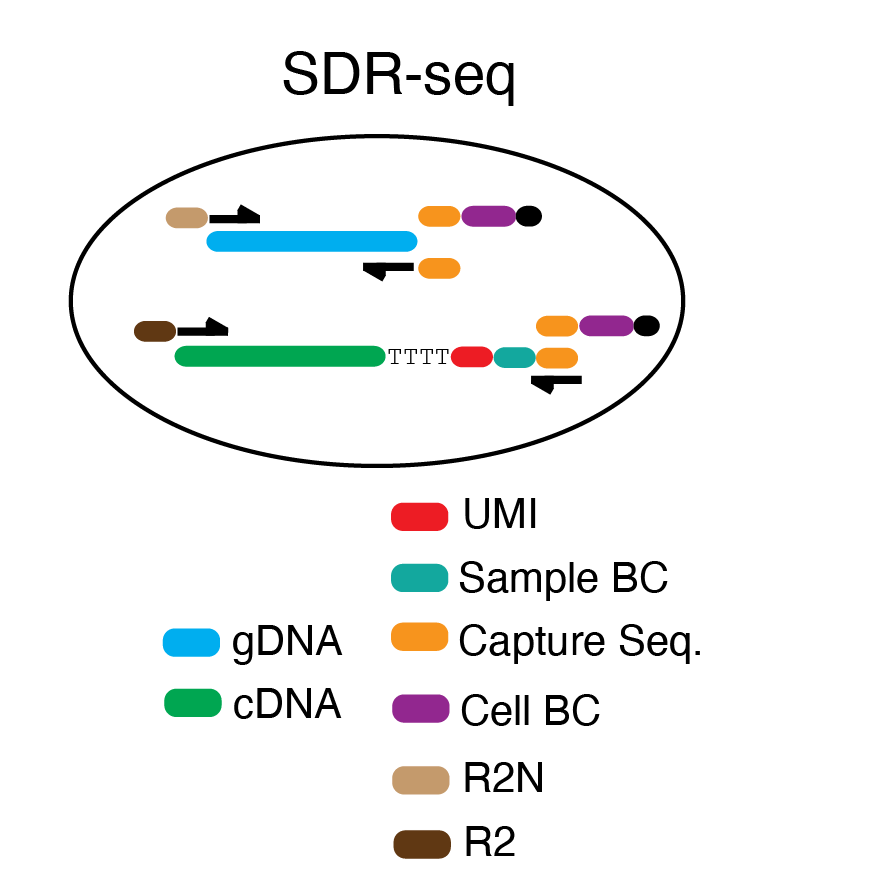
- Dominik Lindenhofer1,2,
- Julia Bauman3,
- John A. Hawkins1,4,
- Donnacha Fitzgerald1,5,6,
- Umut Yildiz1,
- Haeyeon Jung1,
- Anastasiia Korosteleva1,7,
- Mikael Marttinen8,9,
- Moritz Kueblbeck1,
- Judith B. Zaugg10,11,
- Kyung-Min Noh1,12,
- Sascha Dietrich5,13,14,6,
- Wolfgang Huber1,6,
- Oliver Stegle1,4,
- Lars M. Steinmetz1,2,3,15
- 1Genome Biology Unit, European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), Heidelberg, Germany;
- 2DZHK (German Centre for Cardiovascular Research), partner site Heidelberg/Mannheim, Heidelberg, Germany;
- 3Department of Genetics, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, USA;
- 4Division of Computational Genomics and Systems Genetics, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany;
- 5Department of Hematology, Oncology and Rheumatology, Heidelberg University Hospital, Heidelberg, Germany;
- 6Molecular Medicine Partnership Unit (MMPU), European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), Heidelberg, Germany;
- 7Faculty of Biosciences, Heidelberg University, Heidelberg, Germany;
- 8Molecular Systems Biology Unit, European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), Heidelberg, Germany;
- 9Faculty of Medicine and Health Technology, Tampere University, Tampere, Finland;
- 10Structural and Computational Biology Unit, European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Heidelberg, Germany;
- 11Department of Biomedicine, University of Basel | University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland;
- 12Department of Biomedicine, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark;
- 13Department of Oncology, Hematology and Clinical Immunology, Medical Faculty of Heinrich-Heine-Universität, Düsseldorf University Hospital, Düsseldorf, Germany;
- 14Center for Integrated Oncology Aachen-Bonn-Cologne-Düsseldorf (CIO ABCD), Aachen Bonn Cologne Düsseldorf, Germany;
- 15Stanford Genome Technology Center, Palo Alto, CA, USA
- Protocols

Protocol Citation: Dominik Lindenhofer, Julia Bauman, John A. Hawkins, Donnacha Fitzgerald, Umut Yildiz, Haeyeon Jung, Anastasiia Korosteleva, Mikael Marttinen, Moritz Kueblbeck, Judith B. Zaugg, Kyung-Min Noh, Sascha Dietrich, Wolfgang Huber, Oliver Stegle, Lars M. Steinmetz 2025. scDNA-scRNA-seq (SDR-seq). protocols.io https://dx.doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.6qpvr9q43vmk/v1
Manuscript citation:
Lindenhofer, Dominik, Julia R. Bauman, John A. Hawkins, Donnacha Fitzgerald, Umut Yildiz, Jan M. Marttinen, Moritz Kueblbeck, et al. 2024. “Functional Phenotyping of Genomic Variants Using Multiomic scDNA-scRNA-Seq.” bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.05.31.596895.
License: This is an open access protocol distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited
Protocol status: Working
We use this protocol and it's working
Created: January 30, 2025
Last Modified: August 11, 2025
Protocol Integer ID: 119358
Keywords: SDR-seq, single-cell, scDNA-scRNA-seq, scRNA-seq, scDNA-seq, Multiomics, capture sequence to the cdna, rna target, reverse transcription, situ reverse transcription, rna, transcriptomic target, reverse primers for each gdna, multiplexed pcr amplifies gdna, transcriptomic targets in thousand, r2 truseq for rna, containing cdna, scrna, scdna, distinct cell barcode oligo, nextera for gdna, cell barcode oligo, microfluidic tapestri device from missionbio, unique molecular identifier, sdr, microfluidic tapestri device, adding unique molecular identifier, cell barcoding, gdna, single cells per experiment, pcr reagent, cell suspension, sample barcode, reverse primer, single cell, multiplexed pcr, capture sequence, cdna, sequencing depth, cell
Funders Acknowledgements:
HFSP postdoctoral fellowship
Grant ID: LT0023/2022-L
NSF graduate research fellowship
Grant ID: DGE-1656518
Stanford Graduate Fellowship
Grant ID: -
Artificial Intelligence in Health Innovation Cluster
Grant ID: -
German Federal Ministry of Education and Research
Grant ID: SIMONA, 031L0263A
EMBL-GSK collaboration Fund
Grant ID: -
EMBL predoctoral fund
Grant ID: -
Dieter Schwarz Foundation Professorship
Grant ID: -
Abstract
scDNA-scRNA-seq (SDR-seq) is a method that enables a targeted readout of both genomic and transcriptomic targets in thousands of single cells per experiment. It combines an in-situ reverse transcription (RT) step of fixed cells with a multiplexed PCR in an emulsion-based droplets using the microfluidic Tapestri device from MissionBio. A single-cell suspension is fixed with glyoxal, permeabilized and used to perform in-situ reverse transcription. This converts RNA to cDNA while adding unique molecular identifiers (UMIs), a sample barcode (sample BC) and a capture sequence to the cDNA. These cells containing cDNA and gDNA are used as an input for the Tapestri machine where cells are lysed, treated with proteinase K and mixed with reverse primers for each gDNA or RNA target in a first droplet. This droplet is then fused into a second droplet that contains PCR reagents, forward primers containing a capture sequence (CS) overhang and a cell barcoding bead with distinct cell barcode oligos and a matching CS. The multiplexed PCR amplifies gDNA and RNA targets simultaneously in each droplet while cell barcoding is ensured by the complementary CS in the forward primers and the cell barcode oligos. After breaking emulsions, separate NGS libraries for both gDNA and RNA can be generated by having distinct overhangs on the reverse primers (R2N Nextera for gDNA; R2 TruSeq for RNA). This enables to sequence each library at different sequencing depth and length.
Materials
Glyoxal – Sigma #128465
Acetic acid (Glacial) – Sigma #695092
RNasin‱ Ribonuclease Inhibitor – Promega #N2615
Enzymatics Rnase Inhibitor - Enzymatics #280520
IGEPAL CA-630 – Sigma #I8896
Digitonin – ThermoFisher Scientific #BN2006
dNTP-Mix - ThermoFisher Scientific #R0192
Maxima H Minus Reverse Transcriptase - ThermoFisher Scientific #EP0751
Tapestri Single-Cell DNA CoreAmbient Kit v2 - MB51-0007
Tapestri Single-Cell DNA Core -20 Kit v2 - MB51-0010
Tapestri Single-Cell DNA Bead Kit - MB51-0009
Troubleshooting
Design and order oligos
In-situ RT primers
The following oligos need to be ordered to perform the in-situ RT reactions. We recommend ordering at least 8 RT primers for optimal performance of SDR-seq. More RT primers can be ordered in case more samples are required or to improve removal of contaminating ambient RNA reads during analysis.
| A | B | |
| Name | Sequence | |
| RT_primer_1 | GTACTCGCAGTAGTCGACACGTCTCGCCTTANNNNNNNNTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTVN | |
| RT_primer_2 | GTACTCGCAGTAGTCGACACGTCCTAGTACGNNNNNNNNTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTVN | |
| RT_primer_3 | GTACTCGCAGTAGTCGACACGTCTTCTGCCTNNNNNNNNTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTVN | |
| RT_primer_4 | GTACTCGCAGTAGTCGACACGTCGCTCAGGANNNNNNNNTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTVN | |
| RT_primer_5 | GTACTCGCAGTAGTCGACACGTCAGGAGTCCNNNNNNNNTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTVN | |
| RT_primer_6 | GTACTCGCAGTAGTCGACACGTCCATGCCTANNNNNNNNTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTVN | |
| RT_primer_7 | GTACTCGCAGTAGTCGACACGTCGTAGAGAGNNNNNNNNTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTVN | |
| RT_primer_8 | GTACTCGCAGTAGTCGACACGTCCCTCTCTGNNNNNNNNTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTVN |
Overview of 8 RT primers used for in-situ RT reaction. CS: GTACTCGCAGTAGTC; CS extension for universal primer: GACACGTC. Sample barcodes: N701-706
Targeted primer design for gDNA and RNA primers
Targeted gDNA primers were designed using the Tapestri Designer online tool (https://designer.missionbio.com). Targeted RNA primers were selected by taking the “inner primer” sequences designed using the TAP-seq primer prediction tool with at targeted Tm of 60 ° C (min 58 ° C and max 62 ° C) and a product size range from 150-300 bp (https://github.com/argschwind/TAPseq). Two target-specific primers are needed for each gDNA target. Only one target-specific primer is needed for RNA targets, because all RNA targets are amplified by a universal primer binding to the CS + extension introduced via the in-situ RT. Primers designed by the respective design tools require overhangs as described in the table below.
| A | B | |
| Name | Sequence | |
| Droplet_gDNA_fwd | GTACTCGCAGTAGTC-gDNA_specific_sequence | |
| Droplet_gDNA_rev | GTCTCGTGGGCTCGGAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAG-gDNA_specific_sequence | |
| Droplet_RNA_fwd | GTACTCGCAGTAGTCGACACGTC | |
| Droplet_RNA _rev | GTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCT-cDNA_specfic_sequence |
Primers for separate library generation
After breaking emulsions following the multiplexed PCR in emulsion-based droplets library primers with the respective overhangs are required to give specificity for gDNA (R2N) and RNA (R2) targets. gDNA targets will be amplified with library primers containing R1N and R2N binding sequences. RNA targets will be amplified with library primers containing R1N and R2 binding sequences.
| A | B | |
| Name | Sequence | |
| R1N_i5_S502 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACCTCTCTATTCGTCGGCAGCGTC | |
| R1N_i5_S503 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTATCCTCTTCGTCGGCAGCGTC | |
| R1N_i5_S505 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACGTAAGGAGTCGTCGGCAGCGTC | |
| R1N_i5_S506 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACACTGCATATCGTCGGCAGCGTC | |
| R1N_i5_S507 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACAAGGAGTATCGTCGGCAGCGTC | |
| R1N_i5_S508 | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACCTAAGCCTTCGTCGGCAGCGTC | |
| R2N_i7_N701 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTCGCCTTAGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG | |
| R2N_i7_N702 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCTAGTACGGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG | |
| R2N_i7_N703 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTTCTGCCTGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG | |
| R2N_i7_N704 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGCTCAGGAGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG | |
| R2N_i7_N705 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATAGGAGTCCGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG | |
| R2N_i7_N706 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCATGCCTAGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG | |
| R2_i7_N701 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTCGCCTTAGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGT | |
| R2_i7_N702 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCTAGTACGGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGT | |
| R2_i7_N703 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTTCTGCCTGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGT | |
| R2_i7_N704 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGCTCAGGAGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGT | |
| R2_i7_N705 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATAGGAGTCCGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGT | |
| R2_i7_N706 | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCATGCCTAGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGT |
Prepare primer pools for targeted gDNA and RNA amplification
Prepare oligo pools
Forward and reverse oligo pools containing the targeted gDNA and RNA primers were ordered as oPools from IDT (50 pmol/oligo).
Reverse gDNA and RNA oligo pools were diluted to a concentration of 120 µM in H2O each and then mixed 1:1 for usage in Step 2.6 of the Tapestri V2 User Guide.
Forward gDNA oligo pools were diluted to 20 µM. The universal Droplet_RNA_fwd oligo that binds at all RNA targets was also diluted to 20 µM. The forward gDNA oligo pools and the universal Droplet_RNA_fwd oligo were mixed 1:1 for usage in Step 4.8 of the Tapestri V2 User Guide.
Prepare Buffers
All Buffer reactions are calculated for fixation of two sampels. Adjust volumes according to sample number.
Glyoxal fixation buffer0
| A | B | C | D | E | |
| Reagent | Stock | Final (1x) | Volume (µl) | Comment | |
| EtOH (%) | 100 | 20 | 400 | ||
| Glyoxal (%) | 40 | 3 | 150 | ||
| Acetic acid (Glacial) (%) | 100 | 0.75 | 15 | ||
| NaCl (mM) | 5000 | 120 | 48 | ||
| H2O | 1362 | ||||
| NaOH (1M) | 25 | to pH 4 (adjust volume) | |||
| Final Volume | 2000 |
Wash Buffer 1
| A | B | C | D | |
| Reagent | Stock | Final (1x) | Volume (µl) | |
| DTT (mM) | 100 | 1 | 45 | |
| BSA (%) | 10 | 2 | 900 | |
| RNasin Ribonuclease Inhibitor (U/µl) | 20 | 0.04 | 9 | |
| PBS (1x) | 3546 | |||
| Final Volume | 4500 |
Wash Buffer 2
| A | B | C | D | |
| Reagent | Stock | Final (1x) | Volume (µl) | |
| TRIS pH7.5 (mM) | 1000 | 10 | 40 | |
| NaCl (mM) | 5000 | 10 | 8 | |
| MgCl2 (mM) | 1000 | 3 | 12 | |
| Tween20 (%) | 10 | 0.1 | 40 | |
| RNasin Ribonuclease Inhibitor (U/µl) | 20 | 0.1 | 20 | |
| DTT (mM) | 100 | 1 | 40 | |
| BSA (%) | 10 | 2 | 800 | |
| H2O | 3040 | |||
| Final Volume | 4000 |
Permebalization Buffer
| A | B | C | D | E | |
| Reagent | Stock | Final (1x) | Volume (µl) | Comment | |
| IGEPAL CA-630 (%) | 10 | 0.1 | 6 | ||
| Digitonin (%) | 5 | 0.01 | 1.2 | preheat to 65 C for 10 min | |
| Wash Buffer 2 | 592.8 | ||||
| Final Volume | 600 |
Resuspension buffer
| A | B | C | D | |
| Reagent | Stock | Final (1x) | Volume (µl) | |
| DTT(mM) | 100 | 1 | 10 | |
| BSA (%) | 10 | 2 | 200 | |
| RNasin Ribonuclease Inhibitor (U/µl) | 20 | 0.3 | 15 | |
| 1x PBS | 775 | |||
| Final Volume | 1000 |
Dissociation - Fixation - Permeablization
Dissociation
Prepare single cell suspension according to cell line or tissue requirements as for other single cell technologies. Filter cell suspension through a 40 µm cell strainer.
We recommend using 1.5x10^6 cells as input for fixation. We tested performance of SDR-seq with a minimum of 0.35x10^6 cells as input for fixation. Resuspend cells in 1 ml DPBS -/-. To proceed with sampels viability should be >85 %.
Example of cells before fixation using Countess II
Fixation
We recommend using 15 ml Polypropylene centrifuge tubes and swinging bucket rotors in the appropriate centrifuges to minimize cell loss during this process.
Spin cells at 300g for 5 min and remove supernatant.
Resuspend cells in 200 µl of glyoxal fixation buffer (pH adjusted) and incubate at room temperature for 7 min.
Add 1 ml of ice-cold wash buffer 1 and gently invert the tube 2-3 times to mix.
Spin at 400 g for 5 min at 4 ° C and carefully take off supernatant.
Repeat step 7.4 and 7.5 for a total of 2x washes.
Resuspend cells in 175 µl ice-cold permeabilization buffer and incubate on ice for 4 min.
Add 1 ml of ice-cold wash buffer 2 and gently invert the tube 2-3 times to mix.
Spin at 400 g for 5 min at 4 ° C and carefully take off supernatant.
Resuspend cells in 200 µl resuspension buffer.
Filter cell suspension through a 40 µm cell strainer.
Count cells.
Example of cells after fixation using Countess II
Dilute cell suspension to 1.4x10^6 cells/ml
In-situ reverse transcription
We recommend to use a total of 48 wells of a 96-well PCR plate with 10,000 cells/well per experiment during in-situ reverse transcription (RT). This is calculated to have enough surplus for the Tapestri microfluidic device (optimal input ranges from 1.05-2x10^5 cells). Multiple samples can be multiplexed per Tapestri lane by using distinct sample barcodes. We recommend at using at least 8 RT sample barcode primers per SDR-seq experiment to improve removal of ambient RNA during analysis.
Prepare the following RT MM on ice. Mix by pipetting up and down for 10x times.
| A | B | C | D | E | |
| Reagent | Stock | Final | 1x (µl) | 52x (µl) | |
| 5x Maxima H Minus RT Buffer | 5 | 1 | 4 | 208 | |
| Enzymatics Rnase Inhibitor (U/µl) | 40 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 6.5 | |
| RNasin Ribonuclease Inhibitor (U/µl) | 20 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 13 | |
| dNTPs (µM per base) | 10000 | 500 | 1 | 52 | |
| Maxima H Minus RT (U/µl) | 200 | 20 | 2 | 104 | |
| H2O | NA | NA | 0.625 | 32.5 | |
| Total volume per reaction | 8 | 416 | |||
| Final reaction volume | 20 | 1040 |
If using 8 sample barcodes as we recommend prepare the following master mix per sample barcode on ice. Otherwise adjust accordingly.
| A | B | C | |
| 1x (µl) | 6.25x (µl) | ||
| MM RT | 8 | 50 | |
| RT Primer (12.5 µM) | 4 | 25 | |
| Fixed cells (1.4 M/ml) | 8 | 50 |
Add cells last, mix by pipetting up and down 10x.
Aliquot 20 µl of the master mix containing RT primers and fixed cells into the appropriate number of wells into a 96-well plate. In the above example this would be 6 wells per sample barcode.
Put the RT-plate into a Thermocycler that is preheated to 50 °C and run the following program to perform the in-situ RT:
| A | B | C | |
| Tempearture °C | Time | Cycle | |
| 50 | 10 min | ||
| 8 | 12 sec | 3x | |
| 15 | 45 sec | ||
| 20 | 45 sec | ||
| 30 | 30 sec | ||
| 42 | 2 min | ||
| 50 | 3 min | ||
| 50 | 5 min | ||
| 4 | - |
Put the RT plate on ice.
Pool all RT reactions into a 15 ml Polypropylene centrifuge tube containing 10 ml DPBS -/- with 1 % BSA. Make sure to pipet up and down in the RT plate 2-3 times without introducing bubbles to resuspend cells in the RT plate before pooling. Wash each well with 200 µl DPBS -/- with 1 % BSA to reduce cell loss during this step.
Spin cells at 500 g for 10 min at 4 ° C and carefully take off supernatant.
Resuspend in 35-50 µl ice-cold Cell Buffer provided by MissionBio.
Count and dilute cell suspension to 4,500 cells/µl.
Encapsulation, Lysis, Digestion, Barcoding, Targeted PCR and CleanUp
We then followed the Tapestri V2 User Guide Step2 (Encapsulate Cells), Step 3 (Lyse and Digest Cells), Step 4 (Barcode Cells), Step 5 (UV Treatment and Targeted PCR Amplification) and Step 6 (Cleanup PCR Products). gDNA and RNA targets combined were treated as the total amplicon panel size and the specifications of the multiplexed PCR was adjusted according to the recommendations of the Tapestri V2 User Guide.
Library PCR
Library PCR primers were used to amplify separate gDNA (R1N + R2N) and RNA (R1N +R2) NGS libraries.
Set up the following PCR reactions:
PCR – gDNA library
| A | B | |
| Reagent | µl | |
| MisssionBio Library PCR MM (2x) | 25 | |
| Cleaned up sample | 15 | |
| Primer R1N – i5 (2.5 µM) | 5 | |
| Primer R2N – i7 (2.5 µM) | 5 |
PCR – RNA library
| A | B | |
| Reagent | µl | |
| MisssionBio Library PCR MM (2x) | 25 | |
| Cleaned up sample | 15 | |
| Primer R1N – i5 (2.5 µM) | 5 | |
| Primer R2N – i7 (2.5 µM) | 5 |
Run the following PCR cycling program for both libraries on a thermocycler.
| A | B | C | |
| Tempearture °C | Time | Cycle | |
| 95 | 3 min | ||
| 98 | 20 sec | 10x | |
| 62 | 20 sec | ||
| 72 | 45 sec | ||
| 72 | 2 min | ||
| 4 | - |
Follow the library cleanup described in Step 7.7 and the subsequent recommendations in Step 8 (Quantify and Normalize Sequencing Library) in the Tapestri V2 User Guide.
Example Bioanalyzer track of gDNA library.
Example Bioanalyzer track of RNA library.
Sequencing
The separate gDNA and RNA libraries are sequenced with the following read length specifications on Illumina sequencers. Read depth can be adjusted according to experimental needs. We recommend a read depth of at least 10000 reads/cell per 100 amplicons for each library.
gDNA library
| A | B | C | |
| Read | Cycles | Type | |
| R1N | 161 | Cell barcode + gDNA amplicon | |
| R2N | 161 | gDNA amplicon | |
| i5 | 8 | Library PCR sample BC | |
| i7 | 8 | Library PCR sample BC |
RNA library
| A | B | C | |
| Read | Cycles | Type | |
| R1N | 76 | Cell barcode + in-situ RT sample BC +UMI | |
| R2 | 46 | RNA amplicon | |
| i5 | 8 | LibraryPCR sample BC | |
| i7 | 8 | Library PCR sample BC |
Analysis
To generate count matrices for gDNA and RNA libraries please use the package SDRranger. We recommend selecting for high-quality cells first followed by variant calling using the GATK HaplotypeCaller (v4.2.3.0) in each cell separately.
Acknowledgements
We thank all members of the Steinmetz lab for feedback and technical expertise. We thank the Genomics Core Facility (GeneCore) at EMBL for consultation and sequencing. We thank Jan-Philipp Mallm and the Single-cell Open Lab (scOpenLab) at DKFZ for expertise and access to the Tapestri instrument from MissionBio. Support by the DKFZ scOpenLab is gratefully acknowledged. We thank the Flow Cytometry Core Facility at EMBL for support and flow cytometry services. Funding: D.L. received funding from a HFSP postdoctoral fellowship (LT0023/2022-L). J.R.B. is supported by an NSF graduate research fellowship (DGE-1656518) and a Stanford Graduate Fellowship (Smith Fellowship). J.A.H. is supported by the European Research Council (Synergy Grant DECODE under grant agreement no. 810296) and a fellowship through state funds approved by the State Parliament of Baden-Württemberg for the Innovation Campus Health + Life Science Alliance Heidelberg Mannheim. D.F. received funding from a grant from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (SIMONA, 031L0263A). M.K. received funding from an EMBL-GSK collaboration Fund. U.Y. is supported by the EMBL predoctoral fund. L.S.M. is supported by the Dieter Schwarz Foundation Professorship. Work in the Steinmetz lab is supported by a grant from the Else Kröner Fresenius Stiftung (2021_EKS.:61).
