Jun 13, 2025
RNA Library Prep
- Dakota Betz1
- 1ucsd
- Rouse Lab

Protocol Citation: Dakota Betz 2025. RNA Library Prep. protocols.io https://dx.doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.bp2l6nr9zgqe/v1
License: This is an open access protocol distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited
Protocol status: Working
We use this protocol and it's working
Created: March 23, 2020
Last Modified: June 13, 2025
Protocol Integer ID: 34696
Keywords: rna library prep this protocol, rna library prep, kapa mrna hyperprep kit, mrna capture, 1st strand cdna synthesis, cdna synthesis, stranded mrna, rna, total rna, 1ug of intact total rna, intact total rna, wehre dsdna adapter, strand synthesis, second cdna strand, 2nd strand synthesis, combined 2nd strand synthesis, kapa pure beads for reaction cleanup, stranded cdna, resulting dscdna, library amplification, adapter ligation, seq library, library fragment, cdna, carrying appropriate adapter sequence, dscdna, enzyme, specific sequencing, appropriate adapter sequences at both end
Abstract
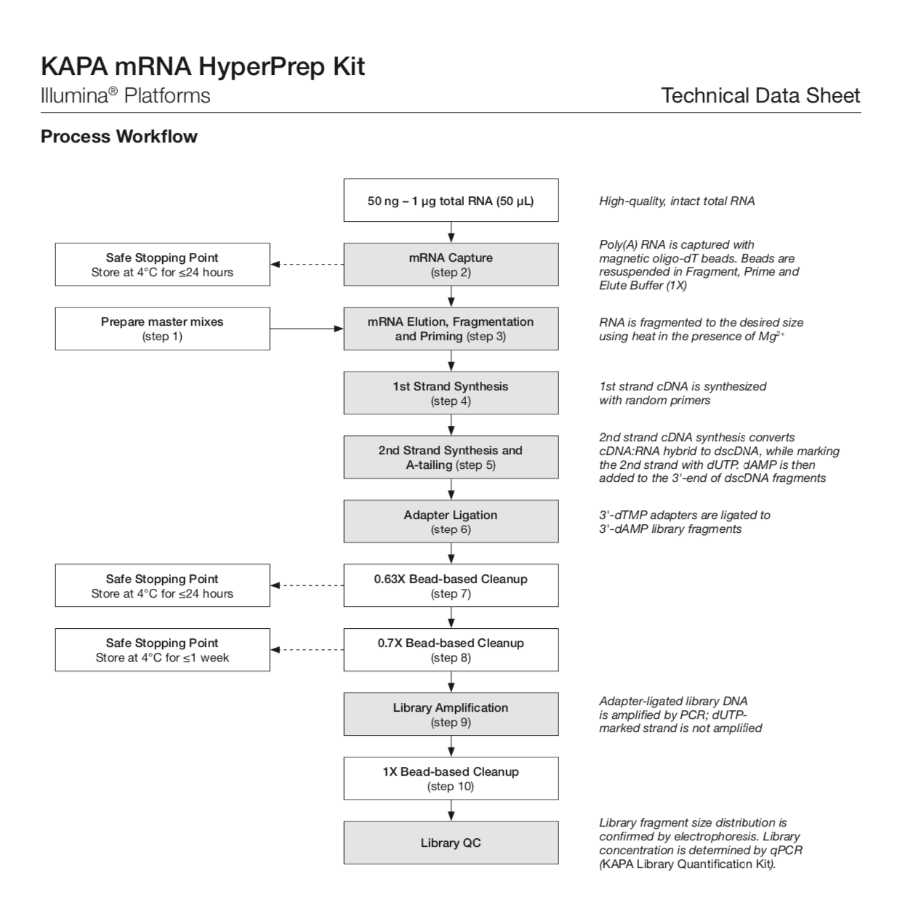
This protocol is for RNA library prep with the KAPA mRNA HyperPrep Kit.
The kit contains all of the buffers and enzymes required for poly(A) mRNA capture and the rapid construction of stranded mrNA-Seq libraries from 50ng - 1ug of intact total RNA via the following steps (below). The kit also provides KAPA Pure Beads for reaction cleanups, along with all of the enzymes and buffers required for mRNA capture, cDNA synthesis, library construction, and amplification. The kit does NOT include RNA or adapters (adapters are sold separately).
1. mRNA capture using magnetic oligo-dT beads.
2. Fragmentation using heat and magnesium.
3. 1st strand cDNA synthesis using random priming.
4. Combined 2nd strand synthesis and A-tailing, which converts the cDNA:RNA hybrid to double-stranded cDNA (dscDNA), incorporates dUTP into the second cDNA strand, and adds dAMP to the 3' ends of the resulting dscDNA.
5. Adapter ligation, wehre dsDNA adapters with 3' dTMP overhangs are ligated to library insert fragments.
6. Library amplification to amplify library fragments carrying appropriate adapter sequences at both ends using high-fidelity, low-bias PCR. The strand marked with dUTP is not amplified, allowing strand-specific sequencing.
Guidelines
Reaction Setup
This kit is intended for manual and automated NGS library construction. To enable a streamlined strategy, reaction components should be combined into master mixes, rather than dispensed separately into individual reactions. When processing multiple samples, prepare a minimum of 10% excess of each master mix to allow for small inaccuracies during dispensing.
Safe Stopping Points
The library construction process from mRNA capture through library amplification can be performed in approximately 5.5 hrs, depending on the number of samples being processed and experience. If necessary, the protocol may be paused safely at the following steps:
- After mRNA Capture (step 2), the resuspended beads may be stored at 4°C for Libraries may be prepared in standard reaction vessels, including PCR tubes, strip tubes, or PCR plates. Always use plastics that are certified to be RNase- and DNase-free. Low RNA- and DNA-binding plastics are recommended.
- 24 hrs in 22 μL of Fragment, Prime and Elute Buffer (2X).
- After 1st Post-ligation Cleanup (step 7), store the resuspended beads at 4°C for ≤24 hrs.
- After 2nd Post-ligation Cleanup (step 8), store the eluted, unamplified library at 4°C for ≤1 week, or at -20°C for ≤1 month.
DNA and RNA solutions containing beads must not be frozen or stored dry, as this is likely to damage the beads and result in sample loss. To resume the library construction process, centrifuge briefly to recover any condensate, and add the remaining components required for the next enzymatic reaction in the protocol.
- To avoid degradation, minimize the number of freeze-thaw cycles, and always store RNA in RNase-free water and DNA in a buffered solution (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0 – 8.5).
Reaction Clean-ups
- This protocol has been validated for use with KAPA Pure Beads. Solutions and conditions for DNA binding may differ if other beads are used.
- Cleanup steps should be performed in a timely manner to ensure that enzymatic reactions do not proceed beyond optimal incubation times.
- Observe all storage and handling recommendations for KAPA Pure Beads. Equilibration to room temperature is essential to achieve specified size distribution and yield of libraries.
- Beads will settle gradually; ensure that they are fully resuspended before use.
- To ensure optimal DNA recovery, it is critical that DNA and KAPA Pure Beads are thoroughly mixed (by vortexing or extensive up-and-down pipetting) before the DNA binding incubation.
- Bead incubation times are guidelines only, and may be modified/optimized according to current protocols, previous experience, specific equipment and samples in order to maximize library construction efficiency and throughput.
- The time required to completely capture beads varies according to the reaction vessel and magnet used. It is important not to discard or transfer any beads with the removal of the supernatant. Capture times should be optimized accordingly.
- The volumes of 80% ethanol for the bead washes may be adjusted to accommodate smaller reaction vessels and/or limiting pipetting capacity, but it is important that the beads are entirely submerged during the wash steps. Always use freshly prepared 80% ethanol.
- It is important to remove all ethanol before proceeding with subsequent reactions. However, over-drying of beads may make them difficult to resuspend, and may result in a dramatic loss of DNA. With optimized aspiration of ethanol, drying of beads for 3 – 5 min at room temperature should be sufficient. Drying beads at 37°C is not recommended.
- Where appropriate, DNA should be eluted from beads in elution buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0 – 8.5). Elution of DNA in PCR-grade water is not recommended, as DNA is unstable in unbuffered solutions. Purified DNA in elution buffer should be stable at 4°C for 1 – 2 weeks, or at -20°C for long-term storage. The long-term stability of library DNA at -20°C depends on a number of factors, including library concentration. Always use low DNA-binding tubes for long-term storage, and avoid excessive freezing and thawing.
Adapter Design and Concentration
- KAPA Adapters are recommended for use with the KAPA mRNA HyperPrep Kit. However, this workflow is also compatible with other full-length adapter designs wherein both the sequencing and cluster generation sequences are added during the ligation step, such as those routinely used in Illumina TruSeq®, Roche® NimbleGen® SeqCap® EZ, Agilent® SureSelect® XT2, and other similar library construction workflows. Custom adapters that are of similar design and are compatible with “TA-ligation” of dsDNA may also be used, remembering that custom adapter designs may impact library construction efficiency. Truncated adapter designs, where cluster generation sequences are added during amplification instead of ligation, may require modified post-ligation cleanup conditions. For assistance with adapter compatibility, ordering, and duplexing, please visit kapabiosystems.com/support.
- Adapter concentration affects ligation efficiency, as well as adapter and adapter-dimer carryover during post- ligation cleanups. The optimal adapter concentration for the workflow represents a compromise between the above factors and cost.
- Adapter quality has an impact on the effective concentration of adapter available for ligation. Always source the highest quality adapters from a reliable supplier, dilute and store adapters in a buffered solution with the requisite ionic strength, and avoid excessive freezing and thawing of adapter stock solutions.
- To accommodate different adapter concentrations within a batch of samples processed together, it is best to vary the concentrations of adapter stock solutions and dispense a fixed volume (5 μL) of each adapter. The alternative (using a single stock solution and dispensing variable volumes of adapter into ligation reactions) is not recommended.
- Adapter-dimer formation may occur when using input amounts lower than the validated range (50 ng). If adapter-dimers are present, as evidenced by a sharp 120 to 140 bp peak in the final library, perform a second 1X bead cleanup post amplification to remove small products. Adapter-dimer formation can be prevented in future library preparations by reducing the amount of adapter in the ligation reaction.
Library Amplification
- KAPA HiFi HotStart, the enzyme provided in the KAPA HiFi HotStart ReadyMix (2X), is an antibody-based hot start formulation of KAPA HiFi DNA Polymerase, a novel B-family DNA polymerase engineered for increased processivity and high fidelity. KAPA HiFi HotStart DNA Polymerase has 5'g3' polymerase and 3'g5' exonuclease (proofreading) activities, but no 5'g3' exonuclease activity. The strong 3'g5' exonuclease activity results in superior accuracy during DNA amplification. The error rate of KAPA HiFi HotStart DNA Polymerase is 2.8 x 10-7 errors/base, equivalent to 1 error per 3.5 x 106 nucleotides incorporated.
- Library Amplification Primer Mix (10X) is designed to eliminate or delay primer depletion during library amplification reactions performed with KAPA HiFi HotStart ReadyMix (2X). The primer mix is suitable for the amplification of all Illumina libraries flanked by the P5 and P7 flow cell sequences. Primers are supplied at a 10X concentration of 20 μM each, and have been formulated as described below. User-supplied primers may be used in combination with custom adapters. For guidelines on the formulation of user- supplied library amplification primers, please contact Technical Support at kapabiosystems.com/support.
- To achieve optimal amplification efficiency and avoid primer depletion, it is critical to use an optimal concentration of high-quality primers. Primers should be used at a final concentration of 0.5 – 4 μM each.
- Library amplification primers should be HPLC-purified and modified to include a phosphorothioate bond at the 3'-terminal of each primer (to prevent degradation by the strong proofreading activity of KAPA HiFi HotStart). Always store and dilute primers in buffered solution (e.g., 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0 – 8.5), and limit the number of freeze-thaw cycles. To achieve the latter, store primers at 4°C for short-term use, or as single- use aliquots at -20°C.
- In library amplification reactions (set up according to the recommended protocol), primers are typically depleted before dNTPs. When DNA synthesis can no longer take place due to substrate depletion, subsequent rounds of DNA denaturation and annealing result in the separation of complementary DNA strands, followed by the imperfect annealing to non-complementary partners. This presumably results in the formation of so-called “daisy chains” or “tangled knots”, comprising large assemblies of improperly annealed, partially double-stranded, heteroduplex DNA. These species migrate slower and are observed as secondary, higher molecular weight peaks during electrophoretic analysis of amplified libraries. However, they typically comprise library molecules of the desired length, which are individualized during denaturation prior to cluster amplification. Since these heteroduplexes contain significant portions of single-stranded DNA, over-amplification leads to the under-quantification of library molecules with assays employing dsDNA- binding dyes. qPCR-based library quantification methods, such as the KAPA Library Quantification assay, quantify DNA by denaturation and amplification, thereby providing an accurate measure of the amount of adapter-ligated molecules in a library—even if the library was over-amplified.
- Excessive library amplification can result in other unwanted artifacts, such as amplification bias, PCR duplicates, chimeric library inserts, and nucleotide substitutions. The extent of library amplification should therefore be limited as much as possible, while ensuring that sufficient material is generated for QC and downstream processing.
- If cycled to completion (not recommended), one 50 μL library amplification PCR—performed as described in Library Amplification (step 9)—can produce 8 – 10 μg of amplified library. To minimize over-amplification and its associated, undesired artifacts, the number of amplification cycles should be tailored to produce the optimal amount of final library required for downstream processes.
- The number of cycles recommended in Table 1 should be used as a guide for library amplification. Cycle numbers may require adjustment depending on library amplification efficiency, presence of adapter- dimer, and the desired yield post-amplification. Quantification of material after the second post-ligation cleanup using a qPCR assay, such as the KAPA Library Quantification Kit, can help to determine the number of amplification cycles required for a specific sample type or application.
| Quantity of starting material (ng) | Number of cycles | |
| 50 - 100 | 13 - 16 | |
| 101 - 250 | 11 - 14 | |
| 251 - 500 | 9 - 12 | |
| 501 - 1000 | 7 - 10 |
Table 1. Recommended library amplification cycles
Evaluating Success of Library Construction
- A specific library construction workflow should be tailored and optimized to yield a sufficient amount of adapter-ligated molecules of the desired size distribution for sequencing, QC, and archiving purposes.
- The size distribution of final libraries should be confirmed with an electrophoretic method. A LabChip® GX, GXII, or GX Touch (PerkinElmer), Bioanalyzer® or TapeStation® (Agilent Technologies), Fragment AnalyzerTM (Advanced Analytical Technologies) or similar instrument is recommended over conventional gels.
- KAPA Library Quantification Kits for Illumina platforms are recommended for qPCR-based quantification of libraries generated with the KAPA mRNA HyperPrep Kit. These kits employ primers based on the Illumina flow cell oligos and can be used to quantify libraries that are ready for flow-cell amplification, and/or were constructed with full-length adapters, once ligation has been completed (i.e., after the post- ligation cleanup or after library amplification cleanup).
- The availability of quantification data before and after library amplification allows the two major phases of the library construction process to be evaluated and optimized independently to achieve the desired yield of amplified library with minimal bias.
Input RNA Requirements
- The protocol has been validated for library construction from 50 ng – 1 μg of purified, intact total RNA in ≤50 μL of RNase-free water.
- The quantity and quality of mRNA in a total RNA preparation can vary significantly between samples. An input of 50 ng – 1 μg of total RNA is recommended to ensure that sufficient mRNA is available for downstream library preparation.
- To minimize 3'→ 5' bias, ensure that RNA is intact and of high quality. The use of fragmented RNA will result in strong bias towards the 3'-end of the mRNA. To determine the quality of RNA, the sample may be analyzed using an Agilent® Bioanalyzer® RNA kit. RNA with a RIN score less than 7 is not recommended for this protocol.
- RNA in volumes >50 μL should be concentrated to 50 μL prior to use by either ethanol precipitation, bead purification (e.g., KAPA Pure Beads or RNAClean® XP beads, Beckman Coulter®), or column-based methods (e.g., RNeasy® MinElute® Cleanup Kit, QIAGEN). Note that some loss of material is inevitable when using any of the above methods to concentrate RNA.
- When concentrating RNA, elute in 55 μL of RNase- free water to ensure that 50 μL is available for use with this protocol.
RNA Handling
- RNases are ubiquitous and special care should be taken throughout the procedure to avoid RNase contamination.
- To avoid airborne RNase contamination, keep all reagents and RNA samples closed when not in use.
- Usealaminarflowhoodifavailable,orprepareasterile and RNase-free area. Clean the workspace, pipettes, and other equipment with an RNase removal product (e.g., RNaseZAP® beads, Ambion Inc.) according to manufacturer’s recommendations.
- To avoid RNase contamination, always wear gloves when handling reagents and use certified RNase-free plastic consumables. Change gloves after making contact with equipment or surfaces outside of the RNase-free working area.
- To mix samples containing RNA, gently pipette the reaction mixture several times. Vortexing may fragment the RNA, resulting in lower quantity and a reduced library insert size.
- To avoid degradation, minimize the number of freeze- thaw cycles and always store RNA in RNase-free water.
mRNA Capture Beads
- Before use, mRNA Capture Beads must be washed and resuspended in mRNA Bead Binding Buffer.
- When preparing multiple libraries, beads may be washed in batches. A single 1.5 mL microtube can accommodate beads for up to 24 libraries. If more than 24 libraries must be prepared, wash the beads in multiple batches.
- When washing a large volume of beads, allow sufficient time for all the beads to collect on the magnet before removing the supernatant. Beads will settle gradually; ensure that they are fully resuspended before use.
- mRNA Capture Beads and mRNA Bead Binding Buffer contain detergent. High speed vortexing and vigorous shaking should be avoided to prevent excessive foaming.
- Before adding the Fragment, Prime and Elute Buffer (2X) to the beads, ensure that all of the mRNA Bead Wash Buffer has been removed. Carryover of mRNA Bead Wash Buffer may inhibit 1st strand cDNA synthesis.
RNA Fragmentation
- RNA is fragmented by incubating at a high temperature in the presence of magnesium before carrying out 1st strand cDNA synthesis.
- After RNA fragmentation, immediately place the heat-treated sample on the magnet and remove the supernatant as soon as the liquid has cleared. Failure to do so may result in rebinding of polyadenylated regions of RNA to the capture beads, resulting in a loss of transcript coverage.
- Fragmentation conditions given in the Library Construction Protocol should be used as a guideline. It is recommended that a non-precious, representative sample of RNA be evaluated for the optimal fragmentation conditions.
For fragmentation optimization beyond what is provided in the Library Construction Protocol, please refer to Appendix: Library Size Distribution Optimization
Materials
Storage Instructions:
- mRNA capture beads and buffers: 2 °C - 8 °C
- cDNA synthesis and library prep reagents: -15 °C - -25 °C
- KAPA Pure Beads: 2 °C - 8 °C in the dark (light sensitive). Do NOT freeze (will damage the beads)
Troubleshooting
Before start
mRNA Capture
- This protocol requires 50 ng – 1 μg of intact total RNA, in 50 μL of RNase-free water. Degraded or fragmented total RNA will result in significant 3'-bias.
- This protocol has been optimized to isolate mature mRNA from total RNA through two subsequent capture steps using mRNA Capture Beads. Other RNA molecules with homopolymeric adenosine regions may also be isolated.
- RNA samples should only be kept on ice where specified in this protocol, since low temperatures may promote non-specific capture, resulting in increased rRNA levels in the captured mRNA.
Bead Washing
Before starting, equilibrate mRNA Capture Beads, mRNA Bead Binding Buffer, mRNA Bead Wash Buffer and Fragment, Prime and Elute Buffer (2X) to room temperature. Before use, beads must be washed with mRNA Bead Binding Buffer (purpose of this section).
Note
Note: This entire protocol takes approximately 8 hrs to complete. Ideally, master mixes for the various steps in the process should be prepared as required. For a streamlined protocol, a reagent master mix with a minimum of 10% excess is prepared for each of these enzymatic steps (use scale feature of this protocol to automatically scale accordingly with appropriate excess). Always ensure that KAPA Pure Beads and PEG/NaCl Solution are fully equilibrated to room temperature before use.
Resuspend the mRNA Capture Beads thoroughly by pipetting up and down gently, or by using a vortex mixer on a low to medium speed setting to prevent foaming. High-speed vortexing or shaking should be avoided to prevent foaming. Refer to Guidelines & Warnings: mRNA Capture Beads for more information.
Transfer 52.5 µL (50 μL + 5% excess for each library to be prepared) of the resuspended mRNA Capture Beads into an appropriate tube. When preparing multiple libraries, beads for up to 24 libraries (1260 μL) may be washed in a single tube. When preparing more than 24 libraries, wash beads in multiple batches. Please refer to Guidelines & Warnings: mRNA Capture Beads for additional recommendations regarding bulk bead washing.
Place the tube on a magnet and incubate at room temperature until the solution is clear. Carefully remove and discard the supernatant, and replace it with an equal volume of mRNA Bead Binding Buffer, 52.5 µL (scaled; 52.5 uL per library).
Remove the tube from the magnet and resuspend the beads by pipetting up and down, or by low to medium speed vortexing. Be careful to avoid producing excessive foam.
Place the tube on the magnet and incubate at room temperature until the solution is clear. Carefully remove and discard the supernatant, and replace it with an equal volume of mRNA Bead Binding Buffer 52.5 µL (52.5 μL per library).
Remove the tube from the magnet and resuspend the beads by pipetting up and down, or by low to medium speed vortexing. Be careful to avoid producing excessive foam.
For each RNA sample to be captured, transfer 50 μL of resuspended mRNA Capture Beads into individual tubes or wells of a plate.
mRNA Capture
To each well/tube from step 8, add 50 μL of the appropriate RNA sample (in RNase-free water). Mix thoroughly by gently pipetting up and down several times.
Place the plate/tube(s) in a thermocycler and perform the 1st mRNA capture as follows:
| A | B | C | |
| Step | Temperature | Duration | |
| 1st mRNA capture | 65°C | 2 min | |
| Cool | 20°C | 5 min |
Place the plate/tube(s) containing the mixture of mRNA Capture Beads and RNA, on a magnet and incubate at room temperature until the solution is clear. Remove and discard the supernatant.
Remove the plate/tube(s) from the magnet and resuspend thoroughly in 200 μL of mRNA Bead Wash Buffer by pipetting up and down several times.
Place the plate/tube(s) on the magnet and incubate at room temperature until the solution is clear. Remove and discard the supernatant.
Resuspend the beads in 50 μL of RNase-free water.
Place the plate/tube(s) in a thermocycler and perform the 2nd mRNA capture as follows:
| A | B | C | |
| Step | Temperature | Duration | |
| 2nd mRNA capture | 70°C | 2 min | |
| Cool | 20°C | 5 min |
Add 50 μL of Bead Binding Buffer to the mixture of mRNA Capture Beads and RNA in each tube, and mix thoroughly by gently pipetting up and down several times.
Incubate the plate/tube(s) at 20°C for 5 min (timer available here: 00:05:00 ).
Place the plate/tube(s) on the magnet and incubate at room temperature until the solution is clear. Remove and discard the supernatant.
Remove the beads from the magnet and resuspend in 200 μL of mRNA Bead Wash Buffer by pipetting up and down several times.
Place the plate/tube(s) on the magnet and incubate at room temperature until the solution is clear. Remove and discard the entire volume of supernatant.
Note
Caution: carryover of mRNA Bead Wash Buffer may inhibit 1st strand cDNA synthesis.
mRNA Elution, Fragmentation, and Priming
Prepare the required volume of Fragment, Prime and Elute Buffer (1X) at room temperature as follows:
| A | B | |
| Component | Volume per sample (uL) | |
| RNase-free water | 11 | |
| Fragment, Prime and Elute Buffer (2X) | 11 | |
| Total volume: | 22 |
Volumes in this table are per sample.
If you've scaled this protocol, your master mix (based on the above table) will need 11 µL RNase-free water and 11 µL Fragment, Prime & Elute Buffer (2X) .
Thoroughly resuspend the mRNA Capture Beads with captured mRNA prepared in step 20 in 22 μL of Fragment, Prime and Elute Buffer (1X) prepared in step 21. Resuspended beads with captured mRNA may be stored at 4°C for ≤24 hrs. Do not freeze the samples as this will damage the beads. When ready, proceed to step 23.
Note
SAFE STOPPING POINT
Place the plate/tube(s) in a thermocycler and carry out the fragmentation and priming program given in the table below:
| A | B | |
| Desired mean library insert size (bp) | Fragmentation | |
| 100 - 200 | 8 min at 94°C | |
| 200 - 300 | 6 min at 94°C | |
| 300 - 400 | 6 min at 85°C |
Immediately place the plate/tube(s) on a magnet to capture the beads, and incubate until the liquid is clear.
Note
Caution: to prevent hybridization of poly(A)-rich RNA to the capture beads, do not allow the sample to cool before placing on the magnet.
Carefully remove 20μL of the supernatant containing the eluted, fragmented, and primed RNA into a separate plate or tube.
Place the plate/tube(s) on ice and proceed immediately to 1st Strand Synthesis.
1st Strand Synthesis
On ice, assemble the 1st strand synthesis reaction as follows (see table). 1st strand synthesis master mix contains 11 µL 1st Strand Synthesis Buffer + 1 µL KAPA Script (scaled; per sample + 20% excess is 11 uL 1st SSB and 1 uL KAPA Script).
| A | B | |
| Component | Volume | |
| Fragmented, primed RNA eluted from beads | 20 μL | |
| 1st strand synthesis master mix | 10 μL | |
| Total volume | 30 μL |
Volumes in this table are per sample.
Keeping the plate/tube(s) on ice, mix thoroughly by gently pipetting the reaction up and down several times.
Incubate the plate/tube(s) using the following protocol:
| A | B | C | |
| Step | Temperature (°C) | Duration | |
| Primer extension | 25 | 10 min | |
| 1st strand synthesis | 42 | 15 min | |
| Enzyme inactivation | 70 | 15 min | |
| HOLD | 4 | (infinite) |
Place the plate/tube(s) on ice and proceed immediately to 2nd Strand Synthesis and A-tailing.
2nd Strand Synthesis and A-tailing
On ice, assemble the 2nd strand synthesis and A-tailing reaction as follows (see table). 2nd strand synthesis and A-tailing master mix contains 31 µL 2nd Strand Marking Buffer +2 µL 2nd Strand Syn. & A-Tailing Enzyme Mix (scaled; per sample + 10% excess is 31 uL 2nd Strand Marking Buffer and 2 uL 2nd Strand Syn. & A-Tailing Enzyme Mix).
| A | B | |
| Component | Volume | |
| 1st strand synthesis product | 30 μL | |
| 2nd strand synthesis and A-tailing master mix | 30 μL | |
| Total volume | 60 μL |
Volumes in this table are per sample.
Keeping the plate/tube(s) on ice, mix thoroughly by gently pipetting the reaction up and down several times.
Incubate the plate/tube(s) using the following protocol:
| A | B | C | |
| Step | Temp. (°C) | Duration | |
| 2nd strand synthesis | 16 | 30 min | |
| A-tailing | 62 | 10 min | |
| HOLD | 4 | (infinite) |
Place the plate/tube(s) on ice and proceed immediately to Adapter Ligation.
Adapter Ligation
Dilute adapters in preparation for ligation, targeting the following concentrations:
| A | B | |
| Quantity of starting material | Adapter stock concentration | |
| 50 – 499 ng | 1.5 μM | |
| 500 – 1000 ng | 7 μM |
On ice, set up the adapter ligation reaction as follows (see table). Adapter ligation master mix contains 40 µL Ligation Buffer +10 µL DNA Ligase (scaled; per sample + 10% excess is 40 uL Lig. Buffer and 10 uL Ligase).
| A | B | |
| Component | Volume | |
| 2nd strand synthesis product | 60 μL | |
| Adapter ligation master mix | 45 μL | |
| Diluted adapter stock | 5 μL | |
| Total volume | 110 μL |
Volumes in this table are per sample.
Keeping the plate/tube(s) on ice, mix thoroughly by pipetting the reaction up and down several times.
Incubate the plate/tube(s) at 20°C for 15 min (timer available here: 00:15:00 ). Proceed immediately to 1st Post-ligation Cleanup.
1st Post-ligation Cleanup
Perform a 0.63X bead-based cleanup by combining the following:
| A | B | |
| Component | Volume | |
| Adapter-ligated DNA | 110 μL | |
| KAPA Pure Beads | 70 μL | |
| Total volume: | 180 μL |
Volumes in this table are per sample.
Mix thoroughly by vortexing and/or pipetting up and down multiple times.
Incubate the plate/tube(s) at room temperature for 5-15 mins to bind DNA to the beads. Optional timers available here: 00:05:00 00:10:00 00:15:00
Place the plate/tube(s) on a magnet to capture the beads. Incubate until the liquid is clear.
Carefully remove and discard 175 μL of supernatant (from each tube).
Keeping the plate/tube(s) on the magnet, add 200 μL of 80% ethanol (to each tube).
Incubate the plate/tube(s) on the magnet at room temperature for ≥ 30s (timer available here: 00:00:30 ).
Carefully remove and discard the ethanol.
Keeping the plate/tube(s) on the magnet, add 200 μL of 80% ethanol (to each tube).
Incubate the plate/tube(s) on the magnet at room temperature for ≥ 30s (timer available here: 00:00:30 ).
Carefully remove and discard the ethanol. Try to remove all residual ethanol without disturbing the beads with a toothpick.
Dry the beads at room temperature for 3 – 5 min (timer: 00:05:00 ), or until all of the ethanol has evaporated. Caution: over-drying the beads may result in reduced yield.
Remove the plate/tube(s) from the magnet. Thoroughly resuspend the beads in 50 μL of 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0 – 8.5) per tube.
Incubate the plate/tube(s) at room temperature for 2 min to elute DNA off the beads (timer: 00:02:00 ). The solution with resuspended beads can be stored at 4°C for ≤24 hrs. Do not freeze the beads, as this can result in dramatic loss of DNA. When ready, proceed to 2nd Post-ligation Cleanup.
Note
SAFE STOPPING POINT
2nd Post-ligation Cleanup
Perform a 0.7X bead-based cleanup by combining the following:
| A | B | |
| Component | Volume | |
| Beads with purified, adapter-ligated DNA | 50 μL | |
| PEG/NaCl Solution | 35 μL | |
| Total volume: | 85 μL |
Volumes in this table are per sample.
Mix thoroughly by vortexing and/or pipetting up and down multiple times.
Incubate the plate/tube(s) at room temperature for 5-15 mins to bind DNA to the beads. Optional timers available here: 00:05:00 00:10:00 00:15:00
Place the plate/tube(s) on a magnet to capture the beads. Incubate until the liquid is clear.
Carefully remove and discard 80 μL of supernatant (from each tube).
Keeping the plate/tube(s) on the magnet, add 200 μL of 80% ethanol (to each tube).
Incubate the plate/tube(s) on the magnet at room temperature for ≥ 30s (timer: 00:00:30 ).
Carefully remove and discard the ethanol.
Keeping the plate/tube(s) on the magnet, add 200 μL of 80% ethanol (to each tube).
Incubate the plate/tube(s) on the magnet at room temperature for ≥ 30s (timer: 00:00:30 ).
Carefully remove and discard the ethanol. Try to remove all residual ethanol without disturbing the beads.
Dry the beads at room temperature for 3 – 5 min (timer: 00:05:00 ), or until all of the ethanol has evaporated. Caution: over-drying the beads may result in reduced yield.
Remove the plate/tube(s) from the magnet. Thoroughly resuspend the beads in 22μL of 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0 – 8.5) per tube.
Incubate the plate/tube(s) at room temperature for 2 min to elute DNA off the beads (timer: 00:02:00 ).
Place the plate/tube(s) on a magnet to capture the beads. Incubate until the liquid is clear.
Transfer 20 μL of the clear supernatant to a new plate/tube(s). The purified, adapter-ligated library DNA may be stored at 4°C for ≤1 week, or frozen at -20°C for ≤1 month. When ready, proceed to Library Amplification.
Note
SAFE STOPPING POINT
Library Amplification
Assemble each library amplification reaction as follows (see table). Library amplification master mix contains 27.5 µL KAPA HiFi HotStart ReadyMix (2X) +5.5 µL Library Amplification Primer Mix (10X) including excess (scaled; per sample without excess is 25 μL KAPA HiFi and 5 μL Primer Mix).
| A | B | |
| Component | Volume | |
| Purified, adapter-ligated DNA | 20 μL | |
| Library amplification master mix | 30 μL | |
| Total volume: | 50 μL |
Volumes in this table are per sample.
Mix well by pipetting up and down several times.
Amplify the library using the following thermocycling profile:
| A | B | C | D | |
| Step | Temp. (°C) | Duration | Cycles | |
| Initial denaturation | 98 | 45 sec | 1 | |
| Denaturation | 98 | 15 sec | **see table below | |
| Annealing* | 60 | 30 sec | **see table below | |
| Extension | 72 | 30 sec | **see table below | |
| Final Extension | 72 | 1 min | 1 | |
| HOLD | 4 | (infinite) | 1 |
*Optimization of the annealing temperature may be required for non- standard (i.e., other than Illumina TruSeq®) adapter/primer combinations.
**See table below for recommended cycle numbers.
Recommended library amplification cycles:
| A | B | |
| Quantity of starting material | Number of cycles | |
| 50 – 100 ng | 13 – 16 | |
| 101 – 250 ng | 11 – 14 | |
| 251 – 500 ng | 9 – 12 | |
| 501 – 1000 ng | 7 – 10 |
Proceed immediately to Library Amplification Cleanup.
Library Amplification Cleanup
Perform a 1X bead-based cleanup by combining the following:
| A | B | |
| Component | Volume | |
| Adapter-ligated DNA | 50 μL | |
| KAPA Pure Beads | 50 μL | |
| Total volume: | 100 μL |
Volumes in this table are per sample.
Mix thoroughly by vortexing and/or pipetting up and down multiple times.
Incubate the plate/tube(s) at room temperature for 5-15 mins to bind DNA to the beads. Optional timers available here: 00:05:00 00:10:00 00:15:00
Place the plate/tube(s) on a magnet to capture the beads. Incubate until the liquid is clear.
Carefully remove and discard 95 μL of supernatant (from each tube).
Keeping the plate/tube(s) on the magnet, add 200 μL of 80% ethanol to each tube.
Incubate the plate/tube(s) on the magnet at room temperature for ≥ 30s (timer: 00:00:30 ).
Carefully remove and discard the ethanol. Try to remove all residual ethanol without disturbing the beads.
Dry the beads at room temperature for 3 – 5 min (timer: 00:05:00 ), or until all of the ethanol has evaporated. Caution: over-drying the beads may result in reduced yield.
Thoroughly resuspend the dried beads in 22 μL of 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0 – 8.5) per tube.
Incubate the plate/tube(s) at room temperature for 2 min to elute DNA off the beads (timer: 00:02:00 ).
Place the plate/tube(s) on the magnet to capture the beads. Incubate until the liquid is clear.
Transfer 20 μL of the clear supernatant to a new plate/tube(s), and store the purified, amplified libraries at 4°C for ≤ 1 week or at -20°C.
Note
END PROTOCOL (SAFE STOPPING POINT)
